Safeguarding private data has become imperative for businesses and individuals alike. With cybercrimes rising, businesses must make the crucial decision between Tokenization and encryption to secure their data. Both processes intend to shield information, but they function in different ways.
Understanding what is the difference between Tokenization and encryption holds the key to making an informed choice.
What is Tokenization?
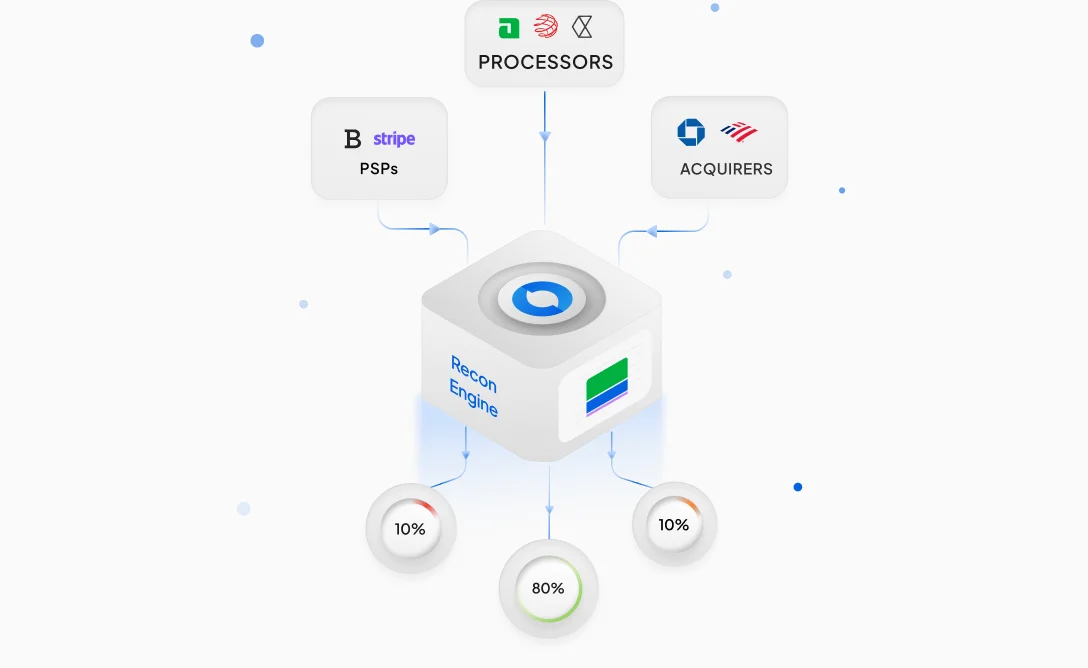
Tokenization is a system that substitutes sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, with random strings of characters called tokens. While such tokens have no inherent value, this adds a unique advantage to them; they cannot be reverse-engineered directly to disclose the original data.
Sensitive data, which is tokenised, is kept safely in another location called a token vault. Popularly deployed in payment systems, Tokenization is particularly useful for reducing the dangers of data breaches or compromises.
Let us take an example. When you make a purchase online, the merchant business doesn’t save the details of your actual card. Instead, Tokenization allows them to save a token that stands for your card. Depending on the system, the token can be used for future transactions without disclosing private information.
The crucial benefit of Tokenization is that it removes the requirement for businesses to save or store sensitive data themselves. This advantage allows businesses to more conveniently ensure compliance with standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Additionally, Tokenization is notably efficient in stopping fraud because tokens can’t be reverse-engineered into their original form without access to the token vault.
What is Encryption?
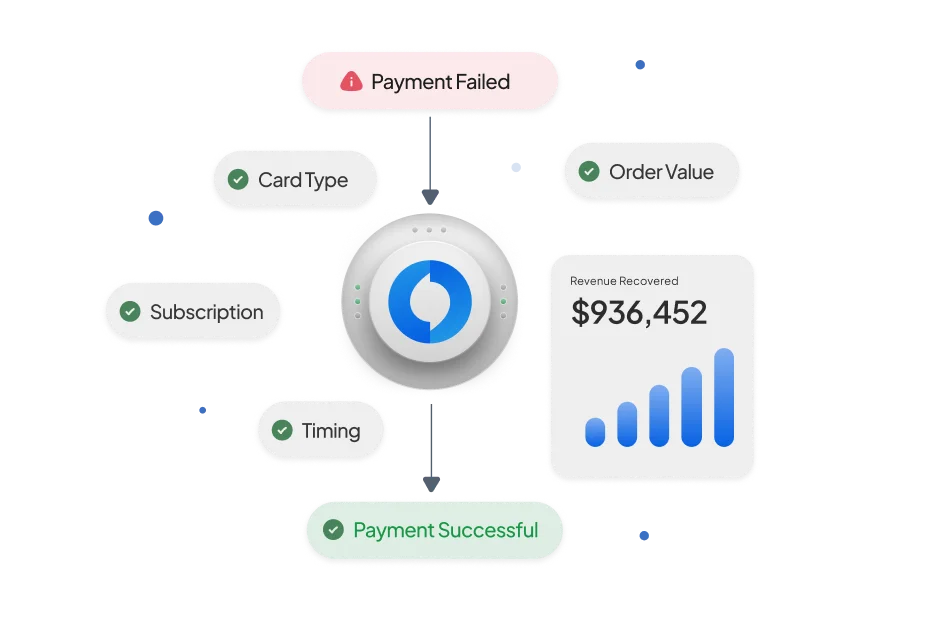
Encryption transforms data into something illegible, utilising an encryption method and a key. Only someone with the correct key can restore the encrypted data to its original form. This system is frequently used to safeguard data.
For instance, when someone keys in their payment information on a website or an app, the encryption system ensures that their details remain guarded as they move between their device and the server. Importantly, the data remains hidden until it arrives at its intended destination, where it is decrypted and used to complete the transaction.
Of course, one major downside of encryption is the danger involved with the management of the encryption key. If a hacker is able to take the encryption key, they can decode the data and get their hands on the original information. In the Tokenization vs encryption debate, the aforementioned disadvantage makes encryption potentially more vulnerable, especially for long-term storage of private data.
Difference Between Tokenization and Encryption
As you do a Tokenization vs encryption comparison, it is important to know that while both aim to guard data, they differ in several key areas.
Below is a comparison that will help you decode the difference between Tokenization and encryption clearly.
| Parameter | Tokenization | Encryption |
| Data Type | Ideal for structured data (e.g., credit card numbers) | Good for both structured and unstructured data |
| Security | Tokens can't be reverse-engineered directly to disclose original data | Data can be decoded if the encryption key is compromised |
| Key Management | Key management is not required | Key management is required |
| Compliance | Streamlines compliance (e.g., PCI DSS) | More effort is needed to meet compliance standards |
| Scalability | Scalable, though complexity increases with large datasets | Easily scalable for large datasets |
| Data Exchange | The exchange of data is easy | Data can be shared securely with key management protocols |
Which is better for your business: Tokenization or Encryption?
As a business, which side do you take in the Tokenization vs encryption debate? The answer depends on your business needs.
If you deal with structured data, such as credit card numbers, Tokenization is the better option. Tokenization streamlines compliance and gives stored data a higher level of safety.
Encryption is the more practical solution if your business handles large volumes of unstructured data, such as documents and images. This is because encryption is well-suited to scalability and offers the ability to safeguard a wider range of data types.
Another factor that you could consider when it is about Tokenization vs encryption, is key management. Tokenization removes the requirement for encryption keys, greatly minimising the danger of data breaches associated with poor key management. However, encryption can provide robust security with careful key management protocols.
Ultimately, the difference between Tokenization and encryption comes down to applications. Tokenization is often the superior choice for securing payment information and lowering PCI DSS compliance burdens. Encryption is the right choice for securing voluminous unstructured data.
Conclusion
When choosing between Tokenization and encryption, study your specific business requirements.
As explained, Tokenization is highly effective for protecting structured data. It also does a better job of reducing compliance burdens.
It can be said that encryption is the more versatile of the two but requires meticulous key management.
Both methods can work in synergy in certain situations, but a good understanding of their strengths and weaknesses will empower you to make the right choice for your business.
Securing sensitive customer data is paramount. Both methods play a role in protecting your business from fraud and data breaches, but Tokenization often leads businesses to manage payment information.
For businesses seeking a secure, scalable solution, Juspay offers advanced Tokenization services to protect sensitive payment data, reduce compliance costs, and improve authorisation rates. Juspay helps merchants optimise their payment processes and enhance security.