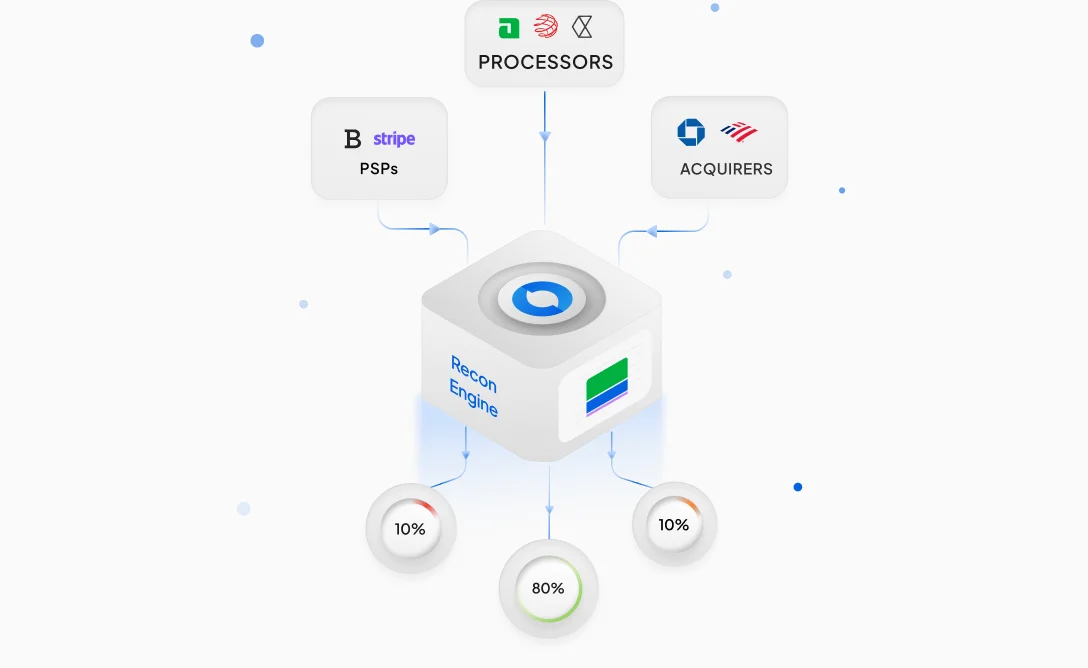
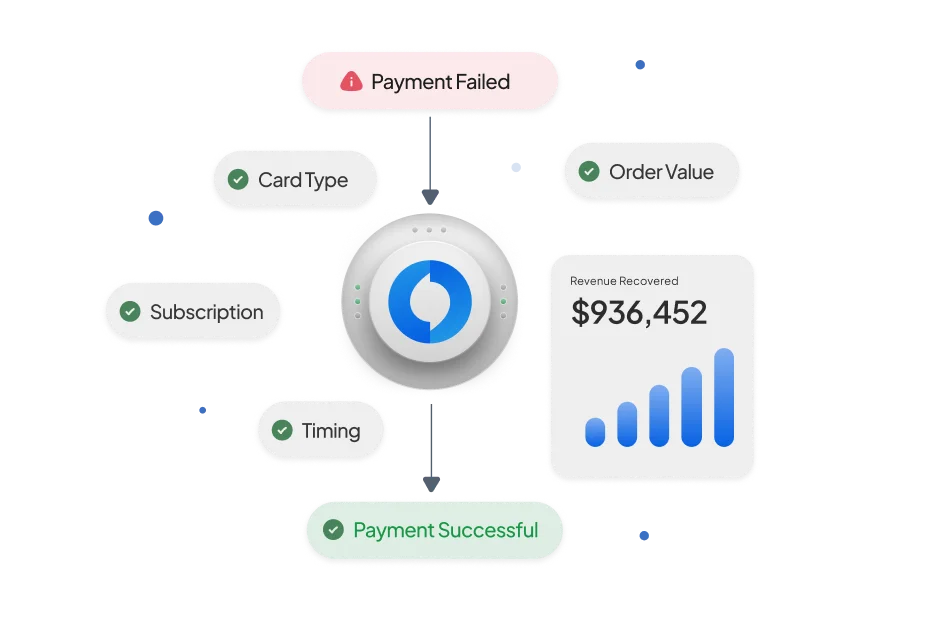
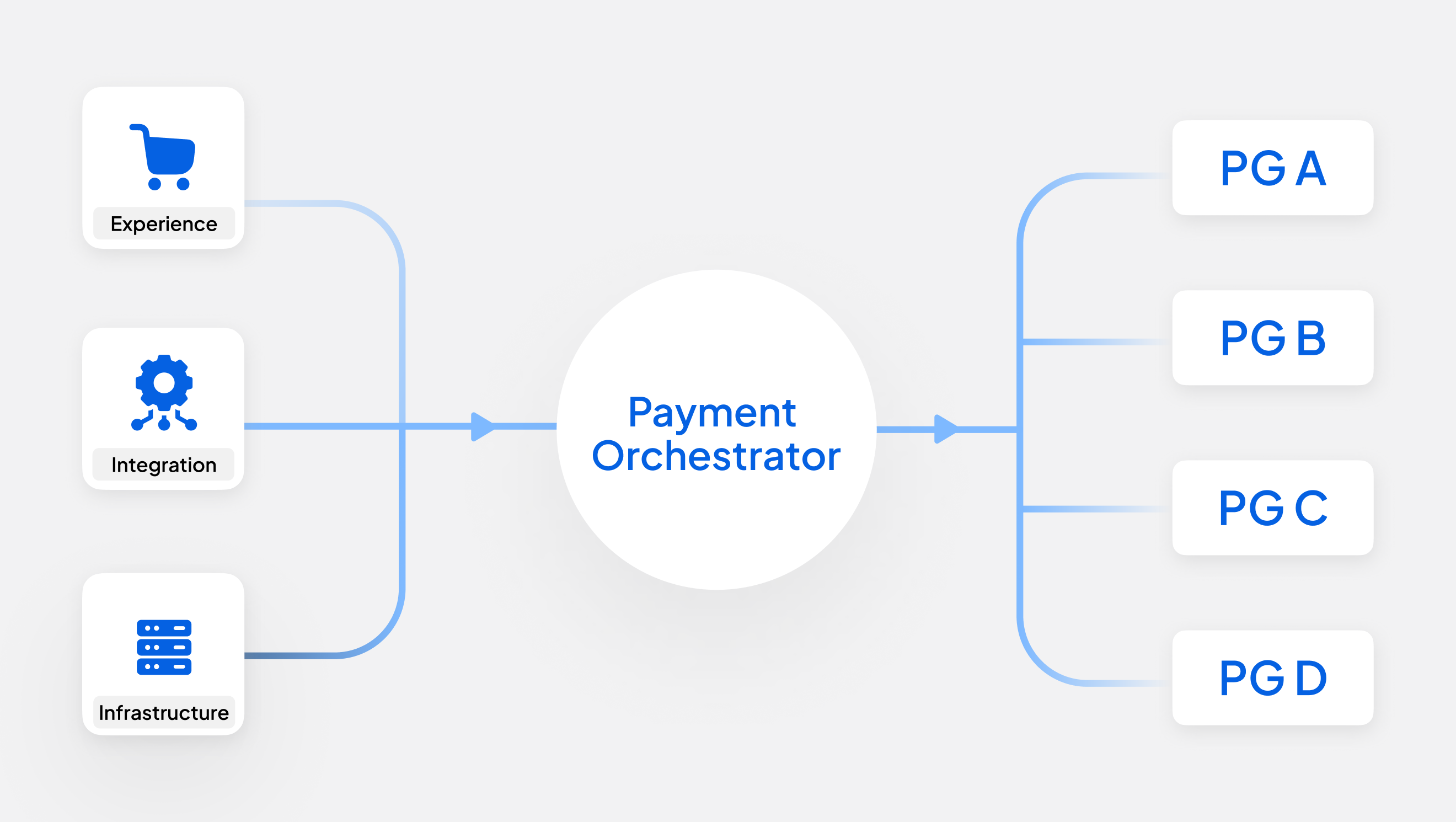
According to a 2019 white paper published by Infosys, the ever-expanding sphere of digital payments is forecasted to reach great heights: a whopping $7.6 trillion globally in 2024. While the digital economy brings with it a host of benefits, one has to contend with the intricacies of securing sensitive personal data. Network tokenization and PCI tokenization seek to enhance security measures while streamlining payment processes for all parties involved in a financial transaction. This article delves deep into the nuances of these two methods of tokenization.
What is Network Tokenization?
To put it concisely, network tokenization replaces confidential card information with a unique token. This token is merchant-specific and transaction-specific, which adds a layer of security by preventing unauthorized use elsewhere. The payment network (for example, American Express or Mastercard) generates this token that stands in for the card details, thus reducing the risk of sensitive data breaches. A hypothetical example of network tokenization is when you buy a dress online, and your payment network generates a token to stand in for your card details. This way, the merchant selling you the dress does not have access to your payment information.
What is PCI Tokenization?
Building on this concept, PCI tokenization involves generating a unique token by a third-party service provider that is compliant with rigorous PCI (payment card industry) standards. On the surface, the process might seem identical to network tokenization, but there is a minute yet crucial difference. A third-party service provider often helps reduce the PCI DSS (Data Security Standard) risk for the business, though some businesses manage PCI tokenization internally. The former has a remote token vault that allows the business to comply with PCI DSS standards and also alleviates the burden of storing reams of confidential payment information. In a nutshell, PCI tokenization generates a third-party token in place of the card details that are stored in a remote vault.
3 Key Differences Between Network and PCI Tokenization
Network tokenization and PCI tokenization share the same end goal: safeguarding sensitive financial information from harmful data exposures. That said, there are a few crucial differences.
- Spectrum: PCI tokenization allows a business to avoid worrying about PCI DSS standards by using a third-party service provider to provide tokens and store confidential card information. Notably, PCI tokens are used for very specific situations within a merchant’s digital ecosystem. Network tokenization offers a secure payment process across multiple transactions, typically tied to specific merchants.
- Oversight: A third-party service provider is contracted by a business to manage token generation in PCI tokenization. By contrast, network tokenization is handled directly by the payment network.
- Everyday application: PCI tokenization works well for businesses looking to lessen the load of complying with PCI DSS standards and overseeing sensitive payment information. Network tokenization suits businesses looking for a uniform and secure payment process across a gamut of merchants.
4 Benefits of Network Tokenization
There is inherent value to network tokenization:
- Since the card information is stored with the payment network, it is in their best interest to create a robust system of network tokenization to nullify data fraud.
- A seamless payment experience is further enhanced when the generated tokens can be used across various merchants and transactions.
- As regulatory oversight becomes even stricter, businesses using network tokenization can reduce the risks associated with sharing confidential financial information during transactions. This improves their compliance levels with best practices.
- In a digital economy where time is money, higher payment decline rates could be detrimental to future growth. Notably, in North America, network tokens have been associated with an average increase in authorization rates of 2.1%.
3 Key Benefits of PCI Tokenization
PCI tokenization has its own share of advantages:
- Since card data, in any shape or form, is not stored directly by merchants, the prime upside to PCI tokens is that they allow a merchant to adhere to strict PCI DSS protocols. This is crucial for a business looking to focus on other areas without being caught up with the gargantuan task of storing and managing sensitive data.
- In April 2024, the International Monetary Fund published a report stating that the global financial sector is one of the main targets for cybercriminals. With PCI tokenization, the risk of data breaches is reduced. One must be aware that data compromises can happen at any time, but tokenization provides an added layer of security.
- Merchants across the world have a number of moving parts to contend with when running a successful business. Bringing in a third-party PCI-compliant service provider allows the merchant to outsource its PCI tokenization, thus streamlining its day-to-day operations.
Choosing the Right Tokenization Method for Your Business
Before a merchant decides between network tokenization and PCI tokenization, they should consider three dimensions. Firstly, their own unique requirements for compliance. Secondly, the breadth of their operations will help pinpoint whether network tokenization or PCI tokenization suits them best. Thirdly, the level of interoperability that each tokenization approach offers.
Juspay prides itself on offering seamless checkout experiences without ever compromising on security. This allows us to offer our clients tokenization solutions that are tailor-made to their requirements. When it comes to the fundamental underpinnings of network tokenization and PCI tokenization, Juspay has you covered, and more. We look forward to helping you scale your online business, one token at a time.