Commerce has always been defined by the interface through which it is conducted. We moved from physical aisles to desktop browsers, and then to the convenience of mobile apps. While these mediums changed where we shopped, the fundamental mechanic remained the same: the user did the heavy lifting of searching, filtering, and clicking through checkout flows.
Today, we are witnessing the next distinct phase of this evolution: Agentic Commerce.
This emerging model represents a fundamental paradigm shift from interface-driven interactions to intent-driven outcomes. In this ecosystem, users no longer navigate complex UI layers; they simply express a goal, and intelligent agents handle the discovery, comparison, and execution.
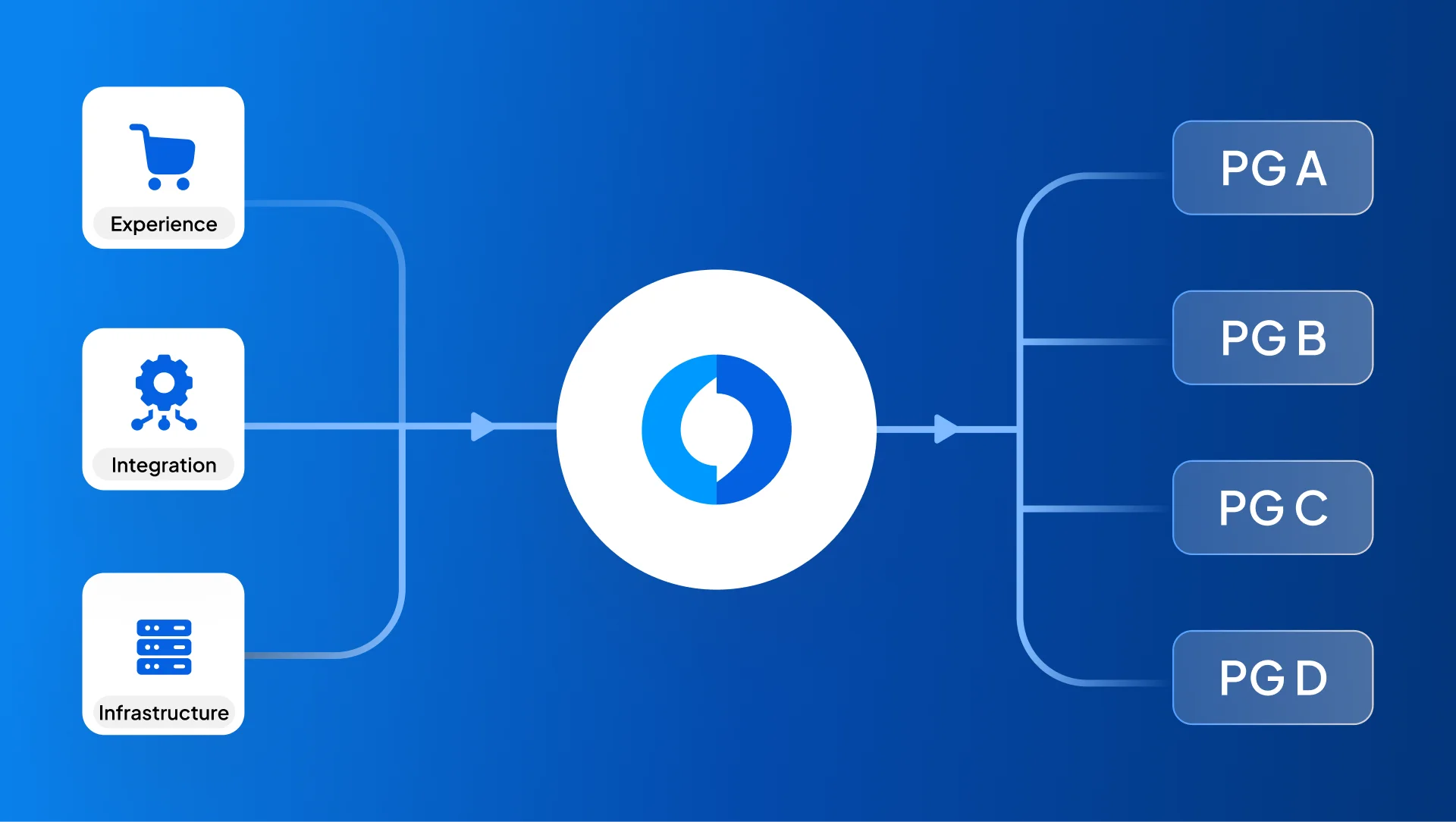
For the ecosystem to function, however, the underlying rails must adapt. For infrastructure providers like Juspay, pioneering this shift is essential. While the challenge is to architect a system where agent-led interactions are seamless, verifiable, and user-controlled, the foundational requirements of trust, authorization, and interoperability remain central even as interfaces evolve.
What Is Agentic Commerce
Agentic commerce refers to purchase experiences where AI agents assist or act on behalf of a user by:
- Interpreting user intent
- Navigating product catalogs
- Preparing carts
- Filling forms
- Completing purchases with proper authorization
- Executing delegated tasks such as reorders or conditional purchases
The common focus is on enabling these interactions in a way that preserves user control, ensures trustworthy execution, and maintains compatibility with commercial and payment systems already in place.
Types of Agentic Commerce
Agentic commerce can be understood using two dimensions. One pertains to human involvement. The other pertains to where the agentic flow occurs. Both dimensions are relevant because different protocols support different combinations.
Dimension 1: Human Presence at Time of Purchase
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Human Present | The user interacts with the agent and approves the final purchase. The agent assists but does not complete orders autonomously. | Product comparison inside a merchant’s app, ChatGPT/Gemini preparing a cart and requesting confirmation. |
| Human Absent (Delegated) | The user gives prior approval or creates a mandate. The agent is allowed to complete purchases automatically under defined conditions. | Auto-replenishment, price-based triggers, ticket buying when sales open. |
Dimension 2: Where the Agent Operates
| Category | Description | Examples |
| Inside the Merchant App | Agentic capabilities embedded within the merchant experience. The merchant controls catalog, UX, and checkout. | In-app AI assistants that help build carts or guide users. |
| On External AI Platforms | Agents such as ChatGPT or Gemini interact with merchant systems through standardized APIs. | Cross-merchant product queries, comparison, and checkout. |
The 2 x 2 View of Agentic Commerce
| Inside Merchant App | On AI Platforms | |
| Human Present | Guided purchase flows in the merchant UI. | User interacts with an external agent and confirms payment. |
| Human Absent | Merchant app executes pre-authorized automated purchases. | External agent performs delegated transactions with verified mandates. |
All four combinations are being explored and have early implementations in different parts of the world.
Foundational Pillars of Agentic Commerce
As agent-driven interactions evolve, industry efforts consistently point toward a common set of principles required to keep these experiences safe, compliant, and trustworthy. These can be understood as the five foundational pillars.
1. Accuracy
Agents must perform only valid and verifiable actions.Every product lookup, cart modification, or checkout step must map to legitimate merchant data. This avoids unintended purchases and ensures agent behavior remains aligned with actual user intent.
2. Anonymity
Agents should not access or store raw payment credentials.Agentic commerce frameworks should rely on tokenization or proxy credential systems so that payment data remains within secure, PCI-compliant domains.
3. Auditability
Maintain comprehensive logging for all agent-initiated steps across their entire lifecycle. Traceable logs are essential for dispute handling, risk analysis, compliance, and debugging.
4. Authentication
Agents must authenticate themselves and support strong customer authentication rules.This may include delegated 2FA or issuer-domain authentication, depending on geography and payment method. Ensuring reliable identity for both agent and user is critical.
5. Authorization
Agents should act only with explicit and scoped user consent.Authorization models can be session-based or mandate-based, with limits, validity periods, and usage controls.
These pillars are consistent across industry specifications and provide the foundation for safe and scalable agentic commerce.
The Value Proposition of Agentic Commerce
Across ecosystem publications and pilot efforts, several recurring benefits are highlighted:
- Reduced friction in discovery and checkout
- More accurate alignment with user preferences
- New commerce surfaces through AI and OS-level platforms
- Delegated commerce for reorders and event-based purchases
- Increased interoperability via standardized schemas and protocols
These advantages are driving experimentation across technology platforms, card networks, merchants, and payment partners.
The Challenges of Agentic Commerce
Although progress is accelerating, several challenges remain central to ecosystem discussions.
- Standardizing Merchant Data
Agents require consistent catalog, pricing, availability, and policy structures. Merchant systems vary widely today.
- Strengthening User Consent
Agent-initiated transactions require strong authorization, scoped constraints, and revocation paths. Signed, cryptographic consent artifacts are under exploration.
- Managing Risk and Liability
Dispute models, fraud handling, and liability assignment are still being evaluated for agent-driven flows.
- Authenticating Agents and Ensuring Trust
Merchants must be confident that a request was genuinely issued by a trusted agent acting on behalf of a real user.
- Avoiding Fragmentation Across Networks
Different networks and platforms are producing different protocols. Interoperability remains a critical goal.
- Preserving User Visibility and Control
Users need clarity on what agents are doing, what is being purchased, and under which conditions.
- Preventing Ranking Bias on External Platforms
Cross-merchant agents must provide transparent and fair product ranking.
- Reducing Merchant Integration Overhead
Merchant adoption depends heavily on how easy it becomes to expose structured APIs and adopt agent-ready checkout flows.
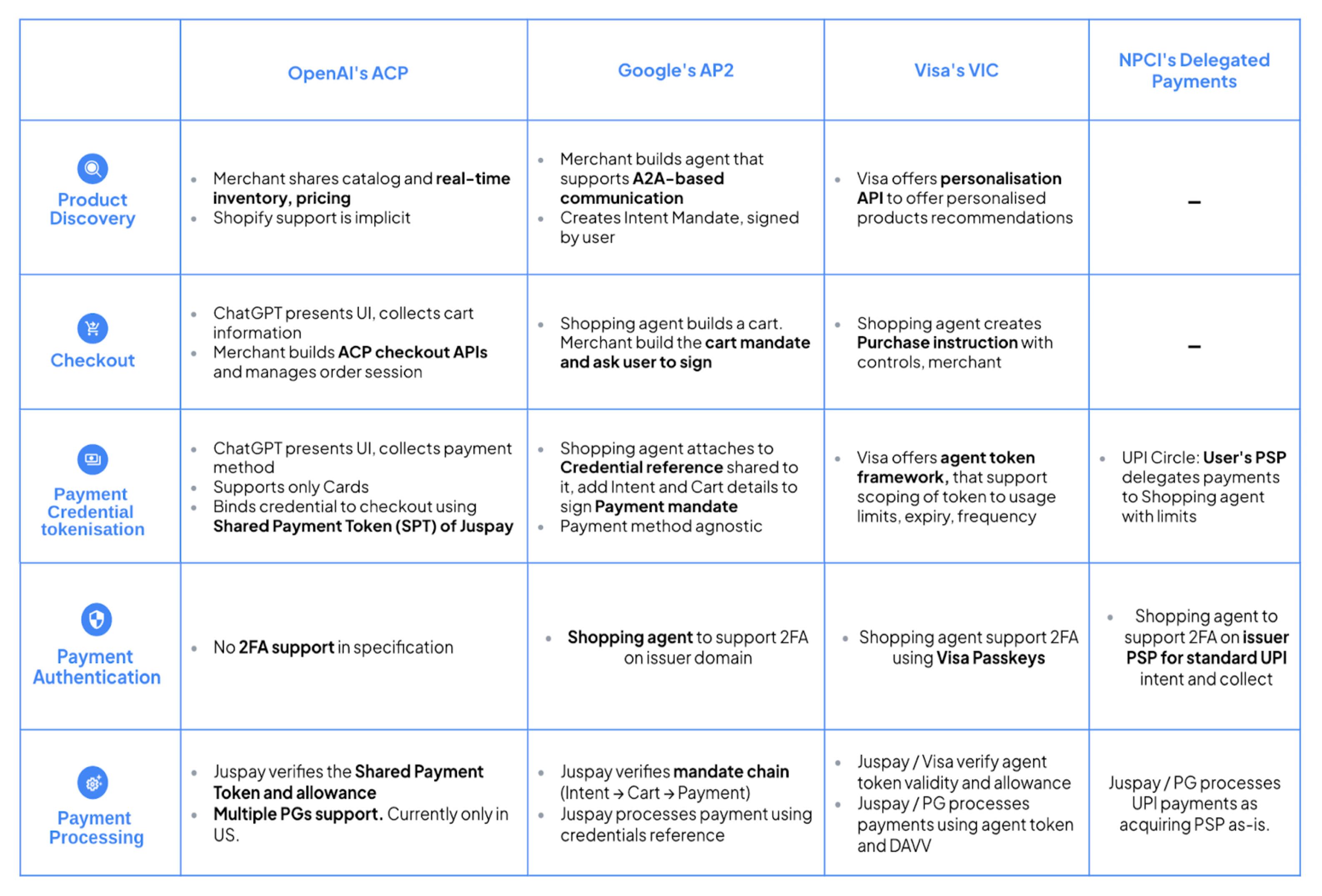
Comparison of Emerging Protocols and Industry Efforts
How Juspay Supports Human Present Agentic Commerce
A large portion of early agentic commerce adoption is expected to occur within merchant applications. These flows are human present, where the user stays inside the merchant app but benefits from agent-driven assistance.
Juspay already supports this mode of agentic commerce through its MCP Server.
Capabilities for Merchant Embedded Agents
Among other things, Juspay MCP allows merchant-embedded agents to:
- Access saved payment methods
- Fetch offers and EMI plans
- Create orders and transactions
- Check order status
- Initiate refunds
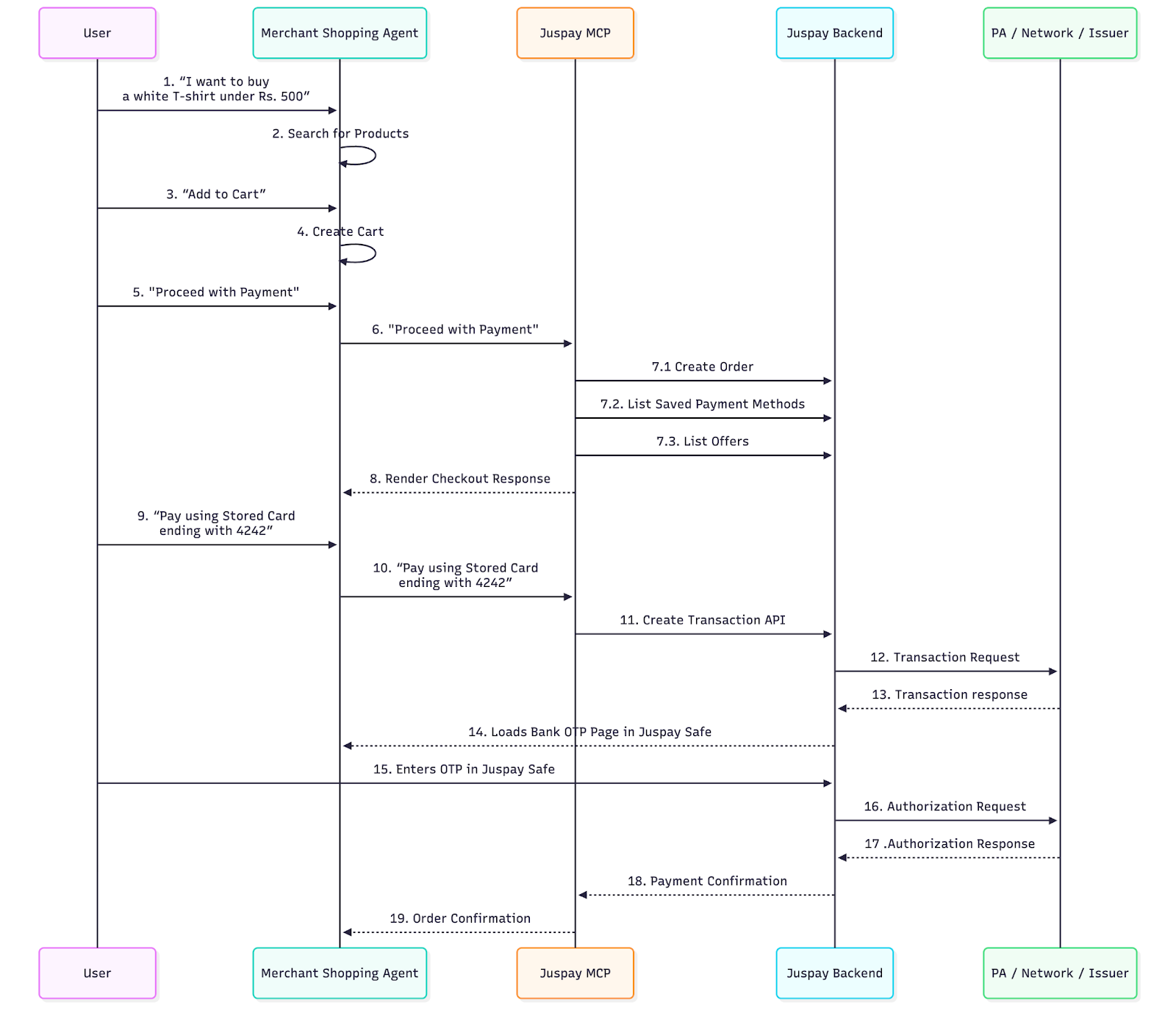
Below is a reference implementation:
This provides a ready-made foundation for agentic shopping experiences without requiring merchants to rebuild their checkout systems.
Why This Matters
Merchant-embedded agents are likely to be among the earliest viable deployments of agentic commerce. By providing secure payment APIs, tokenization, authentication flows, and orchestration across multiple payment gateways, Juspay enables merchants to adopt agentic capabilities without compromising compliance or reliability.
The Next Era of Commerce
Agentic commerce represents a natural evolution in how users express intent and how purchases are executed. While the consumer interface is changing, the underlying needs of commerce remain constant: secure payments, clear authorization, trusted identity, and interoperable systems.
By focusing on the intersection of reliability, safety, and developer experience, Juspay is actively studying these developments and preparing our infrastructure to handle these interaction patterns.as this new model takes shape. Our focus remains on reliability, safety, and developer-friendliness while preparing for the new interaction patterns that agentic commerce will introduce.